1st Year Licence - S.1- Civilization of the Language (Lectures)
Topic outline
-
-
Forum
-
Lecturer: Dr. Salim Kerboua
class: 1st year licence Semester: 1
Introduction
The course introduces the origins and development of English Civilization from the Antiquity to the seventeenth century. The course consists of a series of online lectures that describe and explain the critical periods that shaped the English society. Online lectures are supported by some audio-visual aids such as images, figures, timelines, maps, mindmaps and audio segments of the online lecture given via Google Meet by the teacher (Dr. Kerboua S.)
Course Objectives
The students should be able to understand the historical evolution of English society from prehistory to the Glorious Revolution (1688). They should be able to identify the critical periods and milestones of that history, with its constituting events and key figures.
References and Suggested Readings
The Avalon Project. The Yale Law School website. https://avalon.law.yale.edu/default.aspBrooks, Christopher. (updated in 2020). Western Civilization: A Concise History volume 1.https://docs.google.com/document/d/1awIDaMk3imgceFp12kEwzIl8F8IWJBFdS7xwOt6He_U/edit?pli=1#heading=h.gjdgxsBrooks, Christopher. (updated in 2020). Western Civilization: A Concise History volumes 2 and 3. https://open.umn.edu/opentextbooks/textbooks/698Feudalism. https://courses.lumenlearning.com/atd-herkimer-westerncivilization/chapter/feudalism/Gillingham, John, and Ralph A. Griffiths. Medieval Britain: A Very Short Introduction. Oxford: Oxford U P, 2000.Gravett, Christopher and David Nicolle. The Normans: Warrior Knights and their Castles. Oxford: Osprey, 2006.Internet Ancient History Source Book. https://sourcebooks.fordham.edu/ancient/asbook.aspMorton, A,L. A People’s History of England. London: Lawrence & Wishart, 1996.Medieval Peasants. https://www.medievalchronicles.com/medieval-people/medieval-peasants/medieval-villein-just-images/The Norman Conquest of England and the feudal System. https://www.medievalchronicles.com/medieval-history/medieval-history-periods/the-normans/norman-conquest-of-england-and-the-feudal-system
-
-
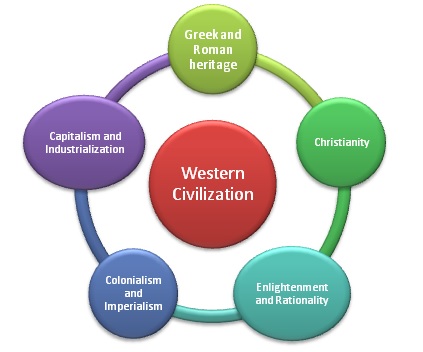
What do we mean by "Western Civilization"? What are its main characteristics?
Objectives
The students should be able to identity the origins and evolution of Western Civilization. They should be able to identify its main characteristics and achievements.
-
What do we mean by "Western Civilization"?What are the roots of Western Civilization?Where to place it in human history?What are the main characteristics of Western Civilization?These are questions this lecture attempts to answer.
-
Characteristics of Western Civilization
-
-
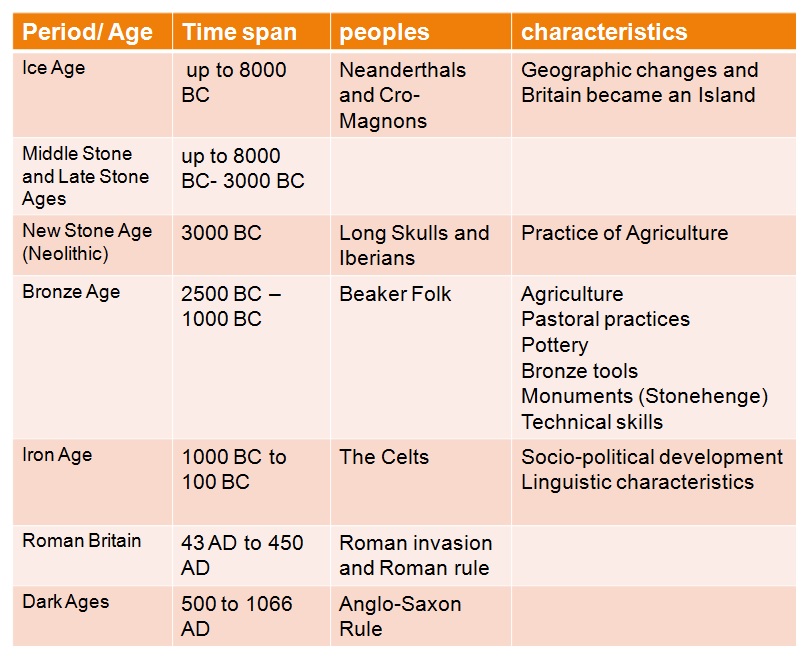
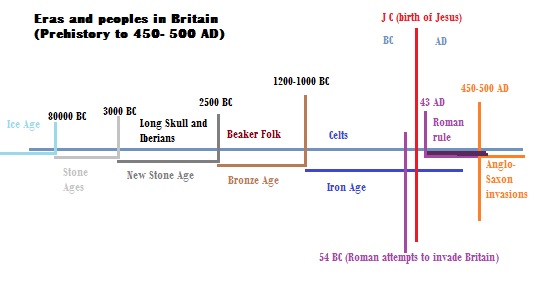
Who were the first settlers of Britain? What ages witnessed what peoples? What did these different peoples bring to Britain? The lectures intends to provide a broad overview of the Ancient Britain, from prehistory, to recorded history, to the Roman rule in the early years of the Christian Era. The lecture emphasizes the settlements and achievements of the Beaker Folk, the Celts, and the Romans.The period under study extends from Prehistory to 450 AD (Christian Era).
Objectives
The students should be able to identify the different settlers that inhabited Britain from the New Stone Age to the Antiquity and the Roman Era. They should be able to point out the main achievements brought by these people.-
- What ages witnessed what peoples?
- The Iberians
- The Beaker Folk
- The Celts
- The Romans
-
-
-
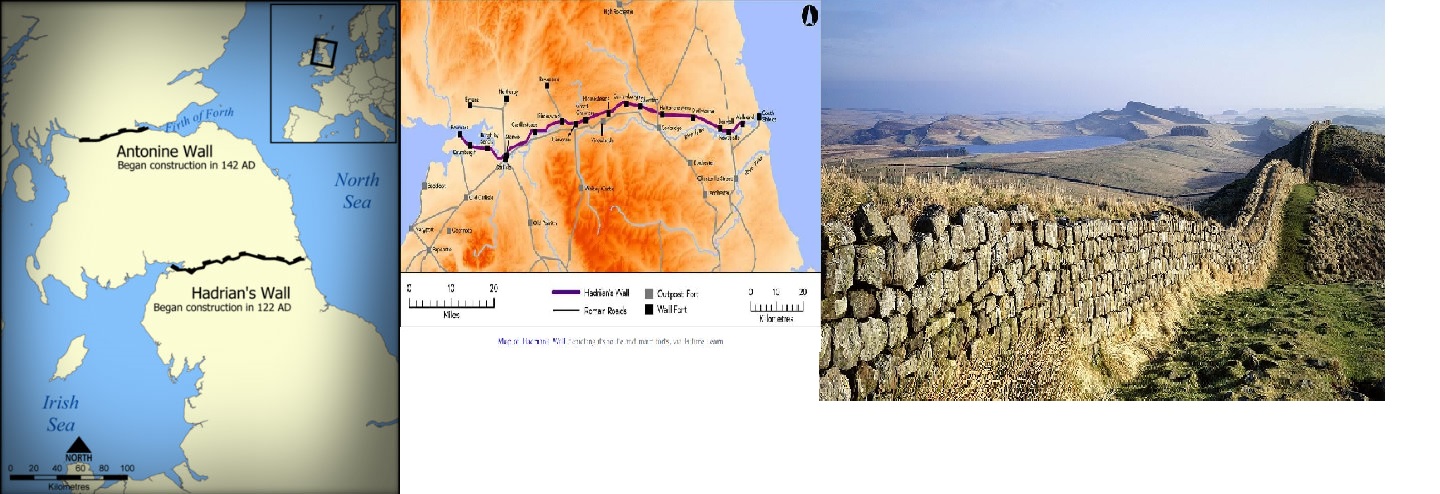
 The different stages of the Roman conquest of Britain (CE = Christian Era)
The different stages of the Roman conquest of Britain (CE = Christian Era) -
Boudicca was a Celtic queen who raised a rebellion against the Romans throughout East Anglia.
-
File
Hadrian's Wall. Roman Emperor Hadrian ordered the construction of a wall to protect the empire from northern threat (the Picts)
-
-
What happened when the Romans left England? Who were the Anglo-Saxons and what happened to the land of Britain when they invaded and settled it? The lecture introduces the Dark Ages (450 - 1066),an unstable period that started with turmoil and permanent warfare but which ended with the christianization and unification of England.
Objectives
The students should be able to identify the origins of the Anglo-Saxons and the different kingdoms they created in Britain. Students should be able to identify the main achievement of Kings Alfred the Great and Athelstan. They should be able to identify the two main achievements of that period: the development of Christianity and the unification and birth of the English kingdom.
-
What happened when the Romans left Britain in 450 AD?Who were the Anglo-Saxons and where did they come from?What was the situation of the land of Britain during the Dark Ages and the Anglo-Saxon rule?What were the most significant milestones of English history during that period (450-1066)?
-
Anglo-Saxons were peoples of German origins. They came from Northern Europe and invaded Britain in the 5th and 6th centuries.
The German invaders were diverse:
- Angles
- Saxons
- Frisians
- Jutes
- Franks
All these peoples were similar in culture and eventually identified themselves indifferently as Angles or Saxons.
-
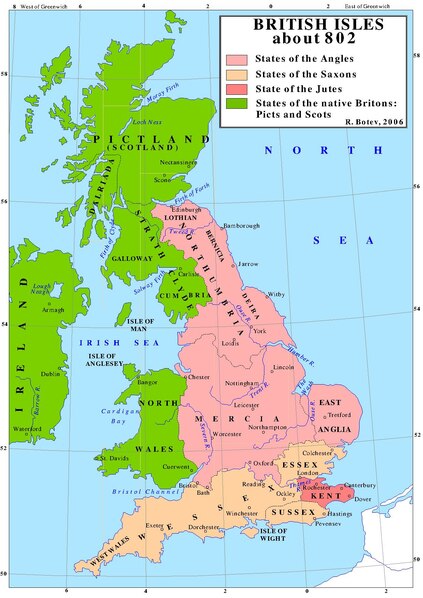 England, ruled by the Anglo-Saxons, in 802.
England, ruled by the Anglo-Saxons, in 802. -
More about the Witenagemot (the Witan), the shire moot, the shire reeve (sheriff), ... (from History Hub YouTube channel)
-
-
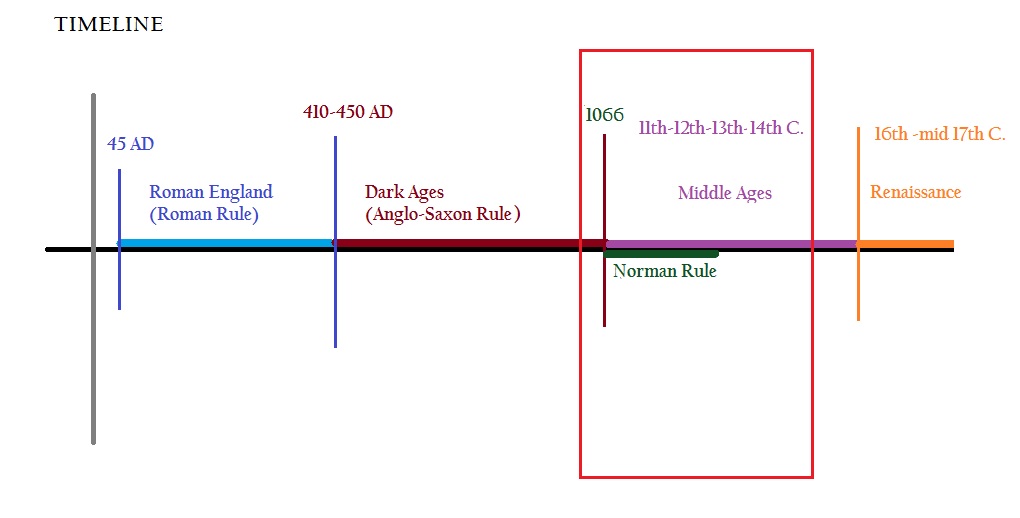
Who were the Normans and What achievements did their rule bring to England? The lecture provides students with a broad overview of the beginning of the Middle Ages with an emphasis on the 1st Dynasty of Norman kings and the introduction of Feudalism in England.
Objectives
By the end of the lecture, the students should be able to identify the changes that were brought to England by the Normans. They should be able to understand the way the feudal system worked during the Middle Ages.
-
-
Who were the Normans? What did they transform English land and society? How was Feudalism important in the Medieval Age (Middle Ages)? This lecture provides an overview of Norman achievements and of the characteristics of the Feudal system during the Middle Ages.
Objectives
The students should be able to identify the main achievements of the Norman rule of England. They should be able to understand why Feudalism came into being and how it worked in the Medieval Age.
-
King Edward I used and developed Parliament. During those times what would become the Parliament was essentially the king's feudal council with a new name and an enlarged membership. The Model Parliament of 1295 consisted of great barons, bishops, abbots, and representatives of counties and towns.
As early as 1258, the Barons rebelled against King Henry and they emphasized the Provisions of Oxford as a way to claim and exercise power. During the following decades, quarrels with the king led the latter to agree on the creation of a body (Parliament) that would counsel the king.
-
-
-
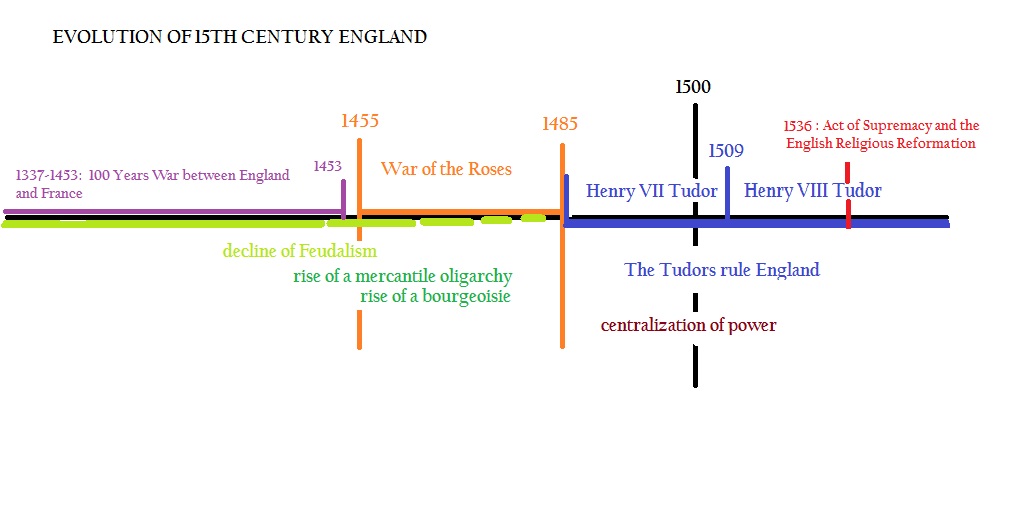
Main characteristics of 15th century England:
- End of the 100 years War between England and France.
- Crisis and decline of the Feudal system
- Crises and conflict within the aristocracy and the monarchy: the War of the Roses (1455-1485)
- rise of a bourgeoisie: a mercantile oligarchy with an expansion of learning among its ranks.
- Coming of a new ruling house: The House of Tudors (Henry VII and his heirs) with a new powerful and centralized government, more and more based on civil servants that do not belong to the aristocracy and nobility.
-
What were the characteristics of the 15th century? The lecture looks into that century of transition from the Middle Ages to the Renaissance; a century which witnessed the decline and end of the Feudal system and which witnessed the rise of a merchant bourgeoisie, the War of the Roses, and the coming of the Tudors with a centralized and powerful monarchy.
-
-
-
What is Anglicanism? Most of the English people are Anglicans. How was the Anglican Church established in England? What were the events that led the English monarchy (Henry VIII Tudor) to break away from the Roman Catholic church? The lecture looks into that fateful period of English history.
-
-
-
Why did the war between the Stuarts and Parliament happen? How did Oliver Cromwell come into power? Did the Restoration fix the political and religious conflict of the 17th century? How did the Glorious Revolution bring an end to the conflict?
The lecture looks into the critical 17th Century events which transformed the English kingdom and established a constitutional and strong parliamentary monarchy.
-
The English Civil War(s)
-
The Glorious Revolution (1688-1689)
from Homeschool History Youtube channel (https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=AnlMS1Hto28)
-