Physics 01/ Mechanics of the material point
Aperçu des sections
-
Material point mechanics is a fundamental branch of physics that studies the motion of objects by considering their mass concentrated in a single point. It is based on Newton's laws, which describe the relationship between the force applied to an object, its mass and its motion. This discipline makes it possible to predict and analyse the motion of objects in a variety of contexts, including free fall, circular motion and the dynamics of particle systems. By combining the concepts of kinematics and dynamics, material point mechanics provides a powerful theoretical framework for understanding the physical world around us. This course is accompanied by illustrations and direct applications so that students can immediately assimilate the concepts covered, thus facilitating the transition from the theoretical course to application problems.
 Course Information
Course Information
The course is one of the fundamental teaching units in the official national programme drawn up by the Ministry of Higher Education and Scientific Research for first-year students in the common core of science and technology, with an hourly volume of
hourly volume : 67h30 half-yearly (Course 3h, TD 1h 30)
coefficient = 03.
Credit : 06.
Evaluation type: continuos control 40% and final exam 60%-
Forum
-
Chat
-
Forum
-
URL
-
URL
-
-
- Dr. Katia. SIDI AHMED
- University: Mohamed khider BISKRA
- Faculty: Sciences and techniques
- Department: Electrical Engineering
- Contact : katia.sidiahmed@univ-biskra
- availabilities : Sunday, Monday, Tuesday 12H00-13H00 by mail : I commit myself to answer by mail in 24 hours following the reception of the message.

-
- Introduce clear definitions and deal with the basic physical quantities that are used to express physical law.
- Determine the kinematic quantities such as the acceleration, velocity and position vectors and the time equation of the trajectory of the material point with respect to a reference frame chosen by the observer.
- Knowledge of the main vector operators used in the expression of the fundamental laws of physics: divergence, gradient and rotational.
- Study the different coordinates (Cartesian, polar, cylindrical and spherical) used to describe and solve problems in three-dimensional systems and analyse complex physical phenomena, particularly in mechanics, electromagnetics and other fields where three-dimensional geometry is important. This course is accompanied by illustrations and direct applications so that students can immediately assimilate the concepts covered, thus facilitating the transition from the theoretical course to application problems.

-
To successfully complete this course, you need to have skills at the level of the final year of secondary education.
- Vectors: Familiarity with vector operations, such as addition, subtraction, scalar product and vector product.
- Kinematics: Knowledge of the concepts of position, velocity and acceleration, as well as motion graphs.
- Vector analysis: Knowledge of vector operators such as gradient, divergence and rotational.

-

-
TestOuvert : mercredi 5 juin 2024, 00:00Terminé : lundi 7 octobre 2024, 00:00
-
Test
-
-
Chapter I: Dimensional analysis and Vector calculus
Chapter II: Kinematics of the material point
Chapter III. Dynamics
Chapter IV. Work and energy
References

-
Fichier
-
Fichier
-
-
the aim of studying physical dimensions is to:
analyse physical relationships
understanding the fundamental units and determination of derived units .


-
Paquetage SCORM
-
Fichier
-
À terminer : mercredi 1 janvier 2025, 19:46
-
TestOuvert : mercredi 25 septembre 2024, 00:00Terminé : vendredi 27 septembre 2024, 00:00
-
Fichier
-
The aim of point kinematics is to study the motion of a point over time independently of the causes that produce the motion. The objectives are to determine kinematic quantities such as acceleration vectors, velocity, position and the time equation of the trajectory of this point relative to a reference frame chosen by the observer
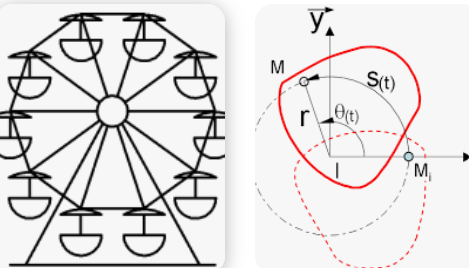
-
Paquetage SCORM
-
Fichier
-
À terminer : mercredi 1 janvier 2025, 19:48
-
TestOuvert : mercredi 25 septembre 2024, 00:00Terminé : vendredi 27 septembre 2024, 00:00
-
Fichier
-
-

-
Fichier
-
TestOuvert : mercredi 25 septembre 2024, 17:00Terminé : vendredi 27 septembre 2024, 19:00
-
-
[1] AHMED FIZAZI, Cahier de la Mécanique du Point Matériel, Office des Publications Universitaires, Algérie, 2013.
[2] ZEBBAR SOUHILA, Mécanique du point matériel cours et exercices, édité par l' institut des sciences et de la technologie du centre universitaire el-wancharissi de tissemsilt, 2018.
[5] ZIANI NOSSAIR et BOUTAOUS AHMED, Mécanique du point matériel cours et
exercices, université des sciences et technologie d’Oran - Mohamed Boudiaf-, 2015/2016.
[6] ALAIN GIBAUD ET MICHEL HENRY, Cours de physique mécanique du point,
Edition Dunod
[7] F. MEKIDECHE – CHAFA, A. CHAFA, A. DERBOUZ, A. DIB, M. HACHEMANE, F.
KAOUAH, Exercices de Dynamique du point.
[8] HADJRI MEBARKI SORIA, Physique générale - live 1: Cinématique du point matériel,OPU, 2016.
[9] HADJRI MEBARKI SORIA, Physique générale - live 2: dynamique du point matériel,OPU, 2016.

